Electrical measuring technology for electromobility – Reliable equipment for high-voltage applications
Electrification is playing an increasingly important role in a wide range of vehicle classes and types. Drive and vehicle components have been subject to far-reaching developments. This applies to batteries in particular, which are continuously being improved in terms of their efficiency, size, charging time, and charging capacity.
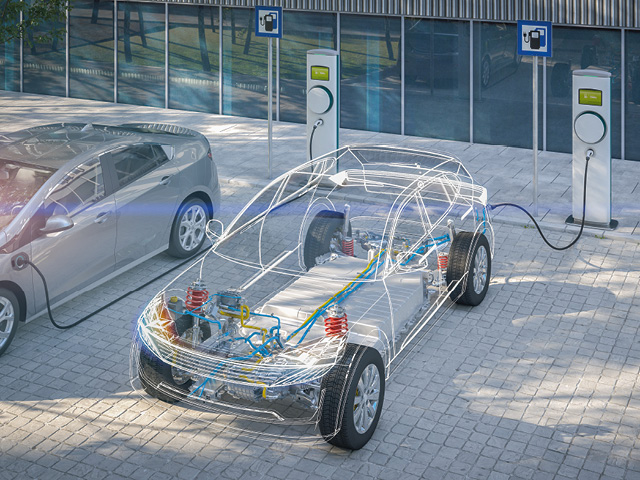

Increasingly stringent requirements for test operations due to increasing battery voltage
To increase vehicle performance, the clear trend is toward higher voltages. Today, cars with a system voltage of 800 V are on the market. Some heavy-duty vehicles achieve voltages of over 1000 V, and systems with 1250 V or 1500 V DC are already in the planning phase. With up to 3.6 kV DC, special-purpose vehicles (e.g., mining vehicles) are even higher. Voltage must be increased in order to enable high charging capacities, since current cannot be randomly increased for reasons of charging cable manageability.
Many high-voltage components that must be tested for function, safety, and reliability in both the development phase and series production are installed in electric and hybrid vehicles. Due to the applicable standards in the automotive industry, comprehensive tests are required for component qualification.
Why Knick?
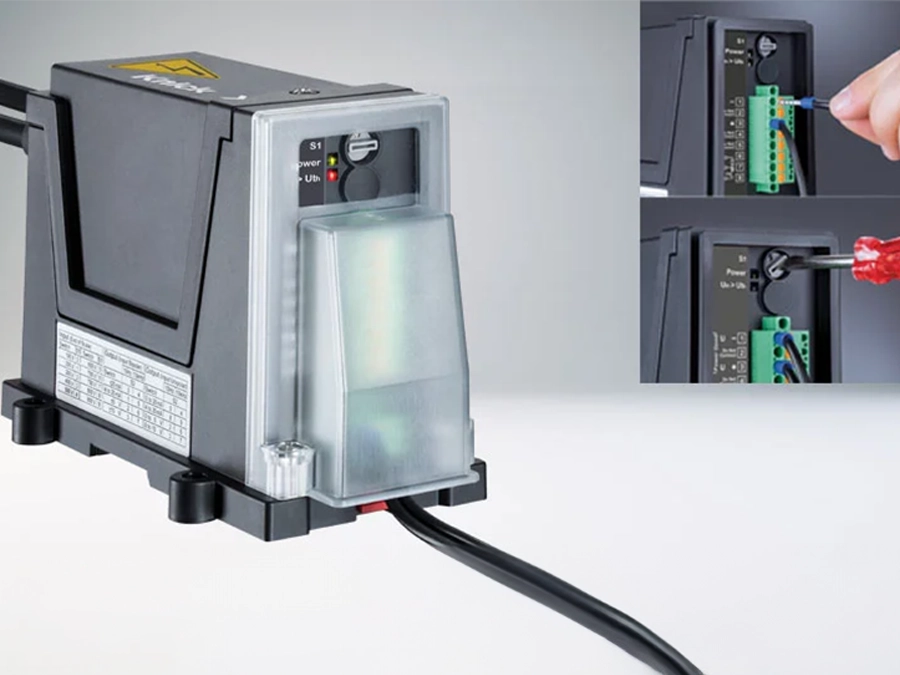
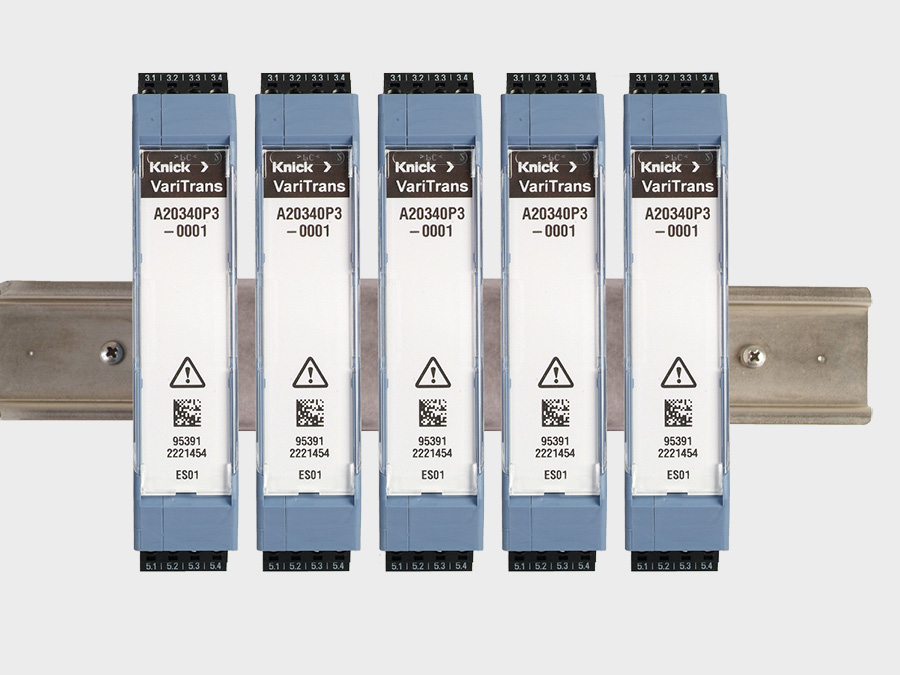
For challenging measuring and testing tasks, Knick offers a comprehensive assortment of high-precision isolating transducers for measuring currents and voltages in the high-voltage range. It also includes highly isolating and fast high-precision transducers for controlling test devices on high electrical potential. Knick offers these properties and specifications in a broad range of standard products, but is also able to develop customer-specific solutions based on the special requirements of an application.
Electric vehicles: High-voltage components
Electromobility requires many electrical measuring technology solutions: for example, for the development, productions, and testing or high-voltage components for electric vehicles (EV), as well as for onboard measurement, energy storage, and the charging process.
- PHIL – Power hardware in the loop emulation
- EOL – End-of-line testing
- Stress screening
Many components must be tested under load. This requires highly dynamic processes like drive emulation to be used. Stress screening is another frequently applied method for detecting failures early on and optimizing components in the development phase. One goal is that all high-voltage components work reliably and safely in their rated voltage range during all imaginable driving situations. Another priority is to shorten production and development times by developing and testing components in parallel without having to finish all neighboring components.
While doing so, special attention is paid to effects like voltage spikes due to abrupt changes in load or coupling capacity. Furthermore, the technology used for signal transmission and isolation must be designed for high voltages in order to exclude all risks for users when running tests in Development or Production. Validation under extreme driving or operating conditions ensures that the specific design of the HV onboard network maintains sufficient reserves for unlimited operation of the vehicle.
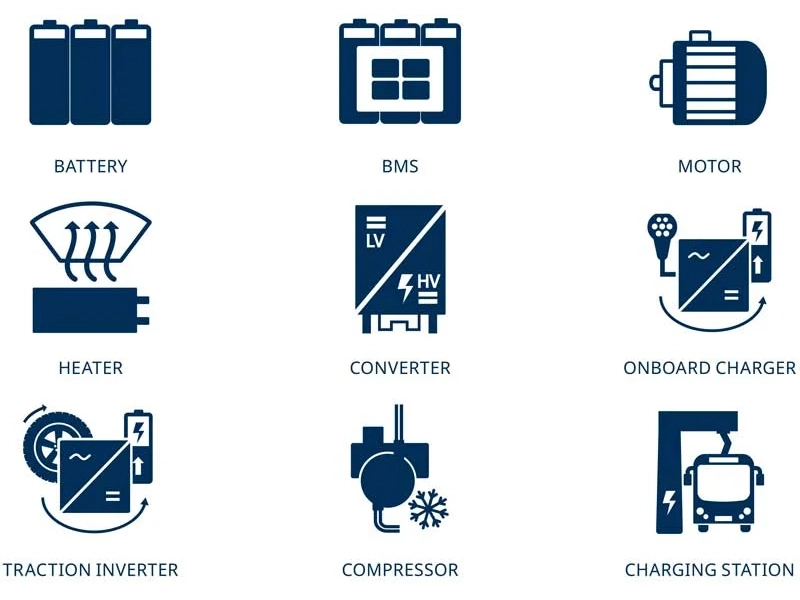
Overview of test and measurement-specific applications and product solutions for electromobility
Associated applications
Do you have more questions? We are here for you.
Contact us!