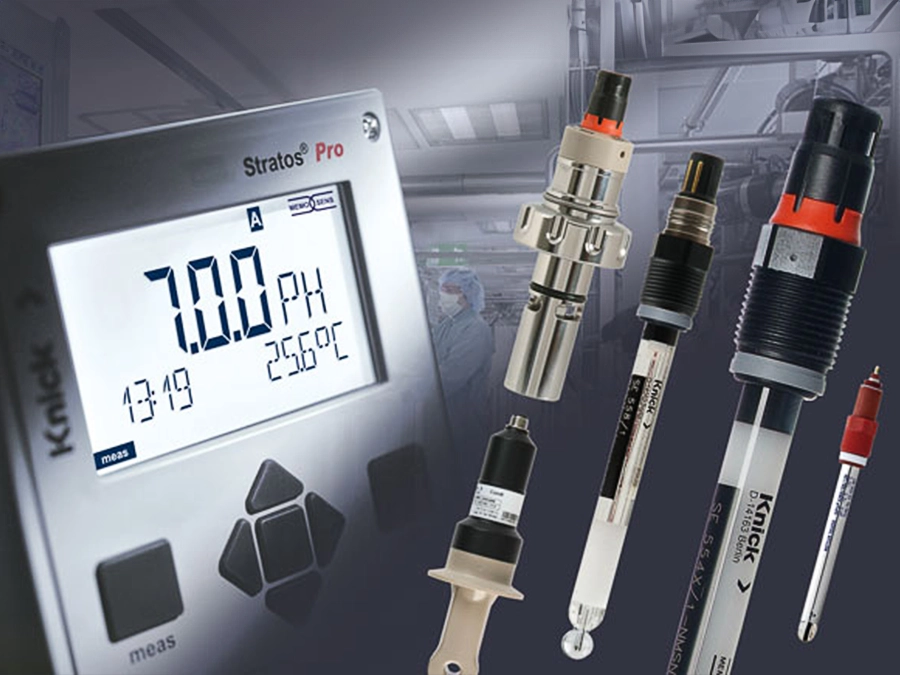
Boiler Feed Water Circuits
Boiler feed water is the central medium for all steam turbines. Feed water is prepared using reverse osmosis and ion exchangers. In boilers, it becomes steam and drives the turbines. Feed water must have a high level of purity in order to avoid corrosion and incrustations in the turbine. Turbine damage is the most cost-intensive incident that can occur in a conventional power plant.
Key Facts About the Application
Sector
Boiler feed water circuits
Application
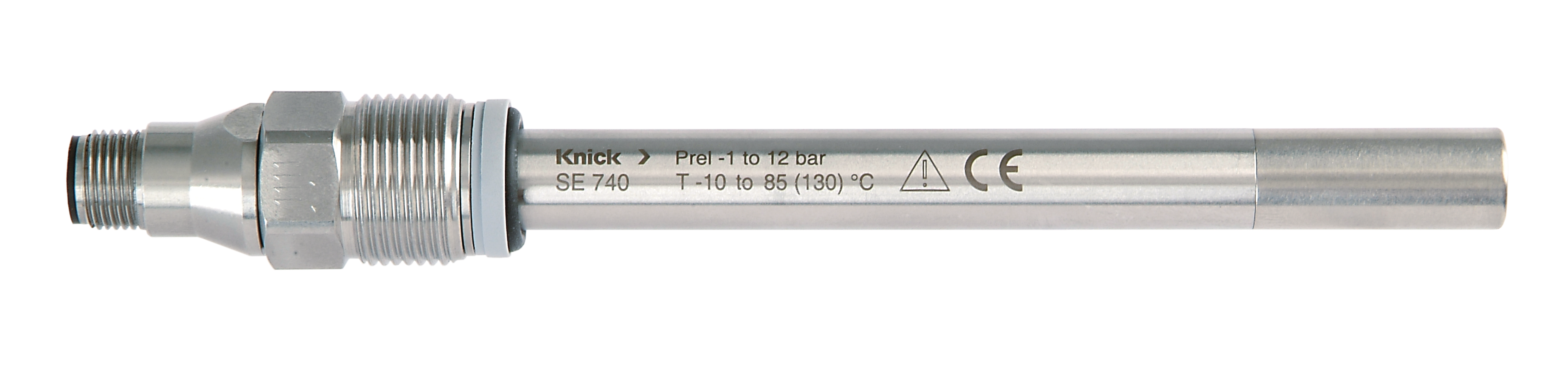
3 applications (1. Checking dissolved oxygen (DO), 2. Checking the pH value and conductivity, 3. Checking the conductivity) at multiple measuring loops
Measured Parameters
pH, conductivity, and ORP
Main Requirements
Low ion concentration
Duplicate conductivity measurement for precise calculation of the pH value
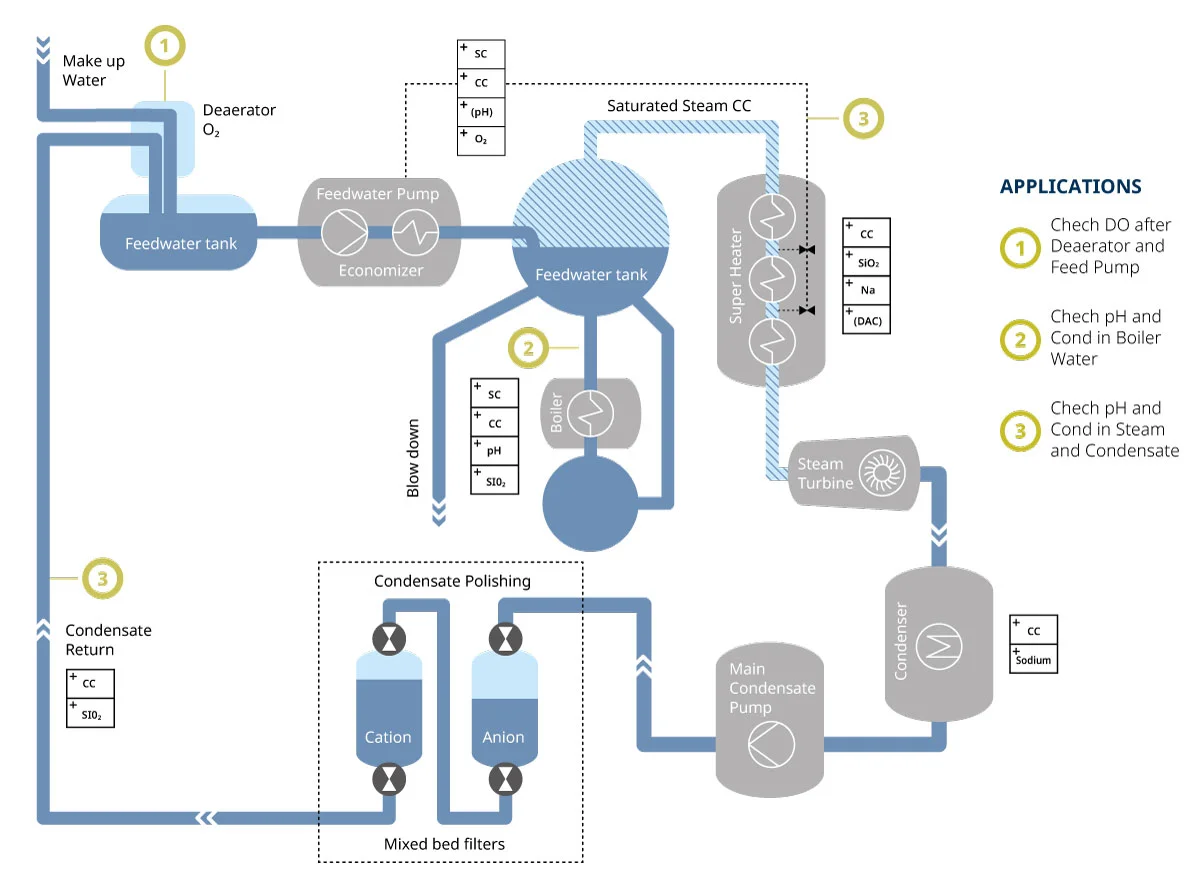
Measurement in Boiler Feed Water, Steam, and Condensate
Description of application
The criteria for the purity of the feed water/condensate are conductivity, pH, and dissolved oxygen. In the schematic, the standard measuring loops for dissolved oxygen, specific conductivity (SC), cation conductivity (CC), degassed conductivity (DAC), and pH are shown. If the condensate return does not meet the specification, it must be bled off. pH and conductivity are the main boiler feed water parameters before entering the turbine.
In most cases, pH and specific conductivity are calculated with the help of dual conductivity measurements. pH and conductivity are the main condensate parameters (after passing through the turbine). Normally, 2-channel conductivity measurements are used to calculate pH, specific conductivity (SC), cation conductivity (CC), and degassed conductivity (DAC).
Since CO₂ in the air can increase conductivity, degassed conductivity is a key criterion for purity.
Requirements for the application
The challenge is the low ion concentration of the medium, which requires duplicate conductivity measurements to precisely calculate the pH value.
Why Knick?
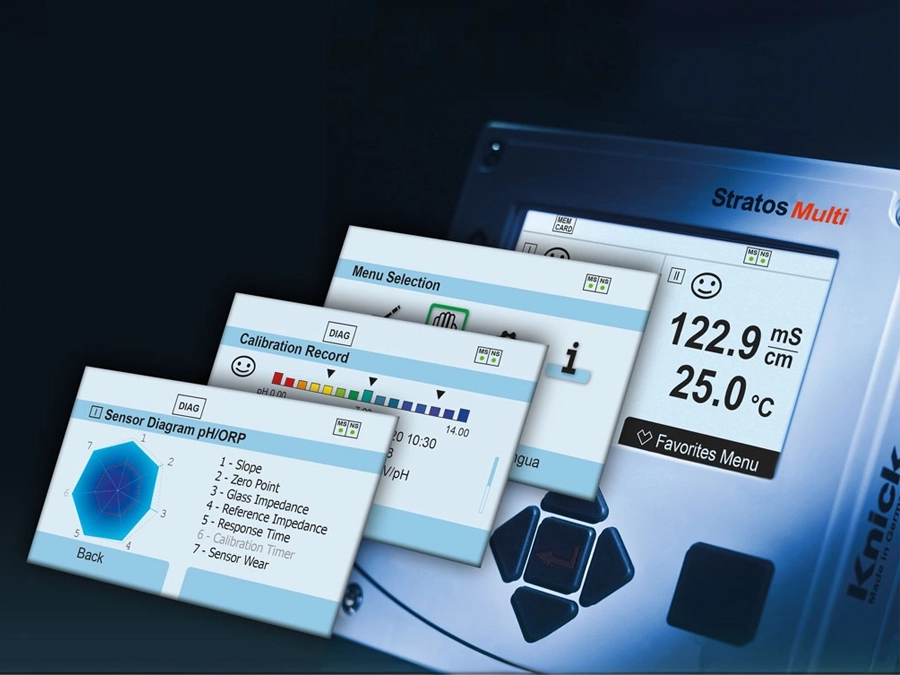
The challenge of the application is the low ion concentration, and metered amine is typically added to protect against corrosion. Amine metering based on conductivity is not particularly easy, however: It requires pH monitoring, which is difficult in view of the low ion content. It is easier to precisely calculate the pH value with the help of duplicate conductivity measurement. Stratos Multi is perfect for this application – after all, duplicate conductivity measurements can easily be combined with a DO measurement for optimal process monitoring.
Associated Products
Associated Industries and Applications
Overview of specific applications and product solutions in different areas of power plants.