PROCESS ANALYTICS
Utilities: Optimization of Liquid Analysis
Utilities: Optimization of Liquid Analysis
In production plants in the process industry, diverse utilities take care of water treatment, steam generation, cooling, and thermal energy recovery. The smooth operation of these utilities is essential for the production process.
Failures in the water supply or steam generation force the main processes to be shut down, leading to considerable extra costs.
In utilities, different chemicals are added to the water in order to prevent biological growth and neutralize corrosive substances. Depending on the application, measurements of the pH value, ORP (or also redox potential), conductivity, and dissolved oxygen are required for metering and process control.
Protecting Industrial Utilities Against Corrosion, Deposits, and Wear
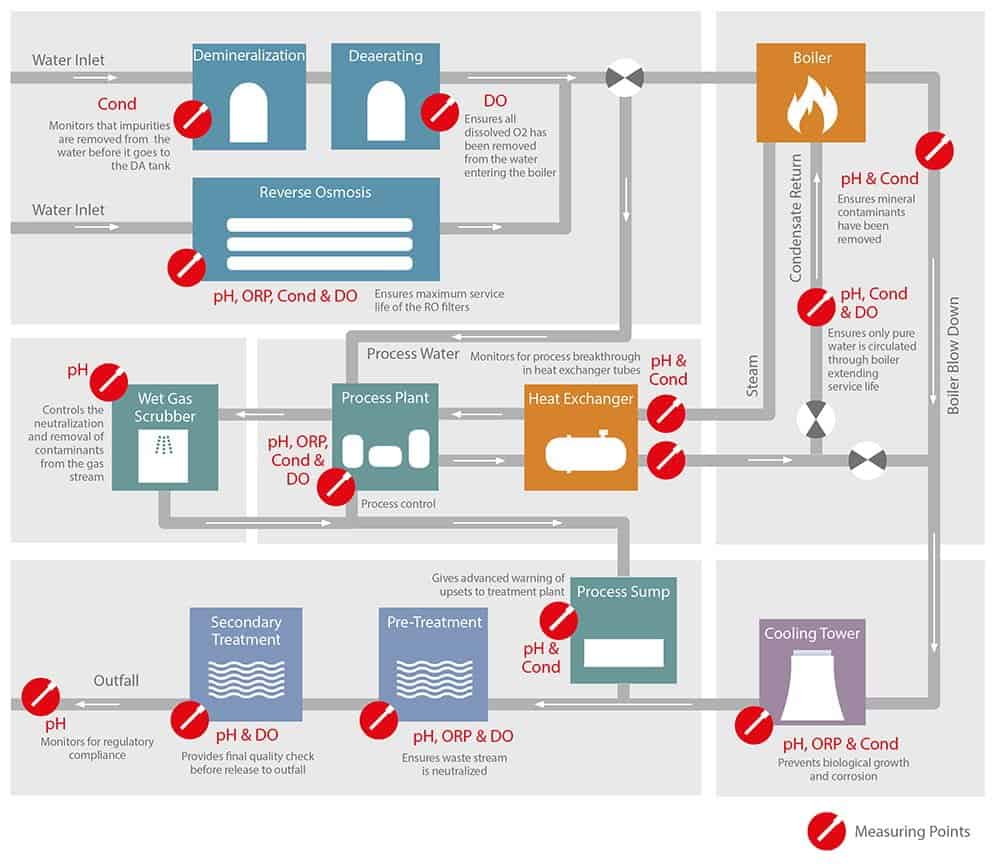
In process industry plants like refineries and pharmaceutical, or chemical factories, many utilities ensure the provision and discharge of the auxiliary media required for the main process. They almost always include water gained from pure or ultra-pure water and steam generated for cleaning and sterilization. Preparing the wastewater created in the process also requires great effort. If the water is to be used in the process, it must first be filtered and disinfected in reverse osmosis systems.
To precisely control the osmosis processes, the degree of water contamination and the retention capacity are determined by conductivity measurements. The proper metering of antimicrobial chlorine additives is ensured based on redox potential measurements. The pH value determines whether or not lime deposits on the osmosis membranes make replacement necessary.
If the water is not used in the process but instead for steam generation, any mineral components must be removed in a full desalination plant and the dissolved oxygen must be removed in degassers before the water enters the steam generator. Accordingly, these processes are controlled by measuring conductivity or dissolved oxygen.
Steam Generation, Heat Dissipation, and Thermal Recovery
Reliable protection of the heating pipes in the steam generator also requires pH, conductivity, and oxygen measurements in the condensate from heat exchangers or cooling towers that is returned to the steam generator circuit. Adding sodium phosphate and sodium hydroxide alkalizes the water in order to minimize corrosion. Other additives like hydrazine, for example, bond oxygen and also reduce corrosion.
To avoid overdosing, which can also lead to problems, the appropriate dosage is regulated through pH and dissolved oxygen measurements. Steam, which is already used to sterilize plant parts, still contains lots of thermal energy. This can be recovered in heat exchangers and provided for other processes.
In terms of heat exchangers, the pipes are among the particularly critical areas. Leaking pipes caused by corrosion can lead to contamination and considerable damage to the plant.
Because the cooled steam precipitates as pure condensation in an intact system, increased conductivity of the condensate indicates the presence of contamination or process breakthroughs caused by corrosion. The process heat from the cooling circuits that is not needed is dissipated through cooling towers. To prevent mineral incrustation on the surfaces here, the pH value of the water is regulated by adding acid. Further, oxidizing agents are added for disinfection and to prevent organic growth in the pipes. The required dosage is determined by measuring redox potential.
Neutralizing Wastewater
Before wastewater can be drained into the public sewage system, it must be subjected to a final treatment until the pH value, dissolved oxygen, and redox potential are all within the permitted range. Process water and the wastewater from gas scrubbers are treated the same way.
Avoiding Measuring Problems in Moist Environments
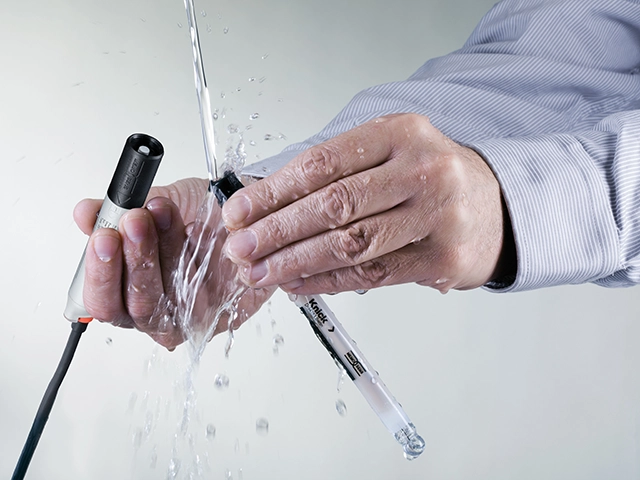
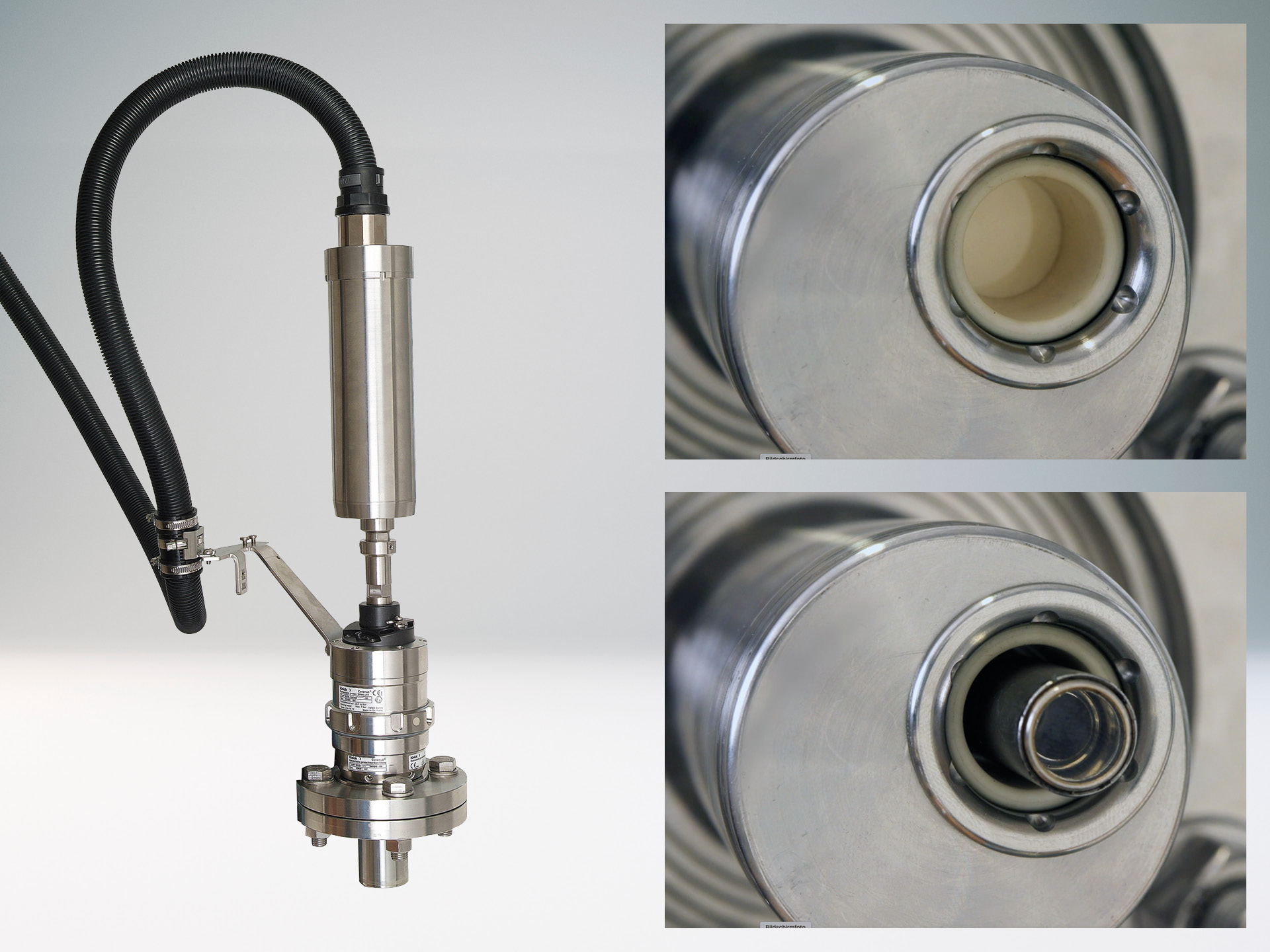
As a rule, measuring loops for utilities in the process industry are exposed to very moist or wet ambient conditions that cause many problems when conventional analog sensors are used. Moisture, corrosion, and deposits on the metal contacts of plug-in connections can lead to drift or distortion of the measured values. However, the alternative of using permanently wired analog sensors increases maintenance costs because every time the sensor is replaced, the cable must be pulled out of the transmitter and rewired when the replacement sensor is in place.
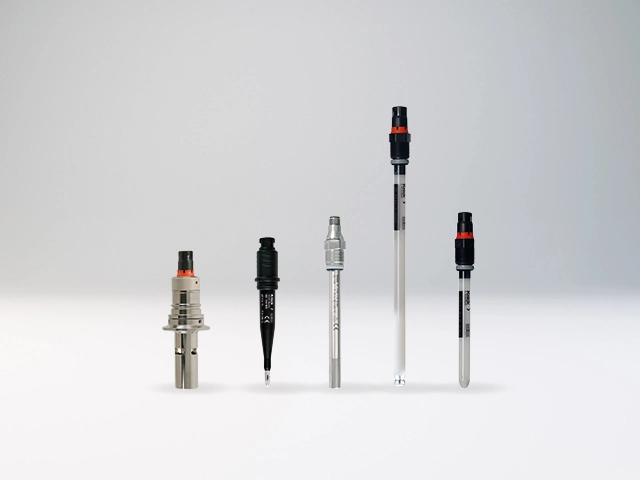
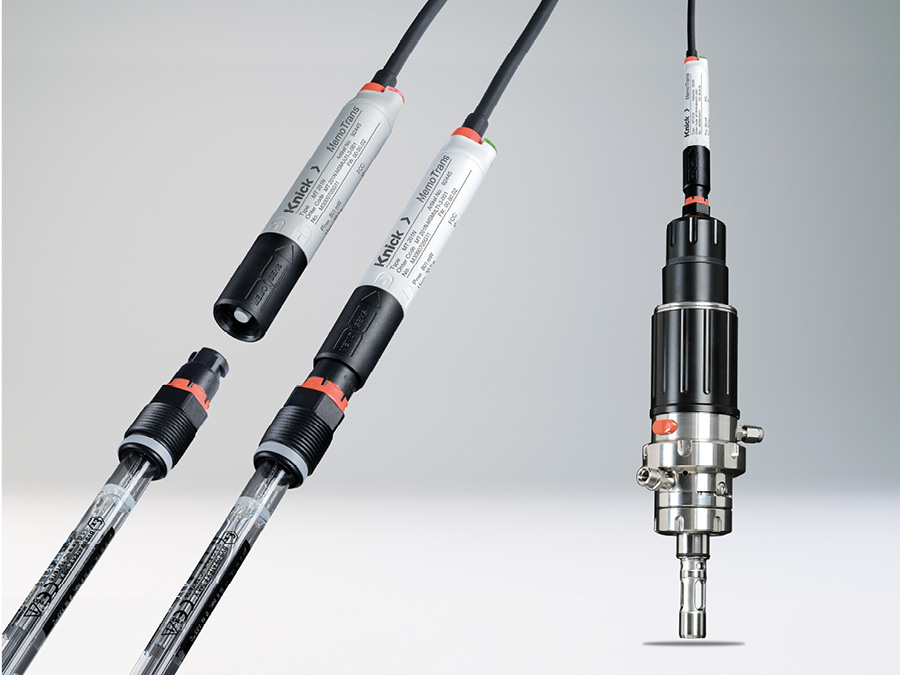
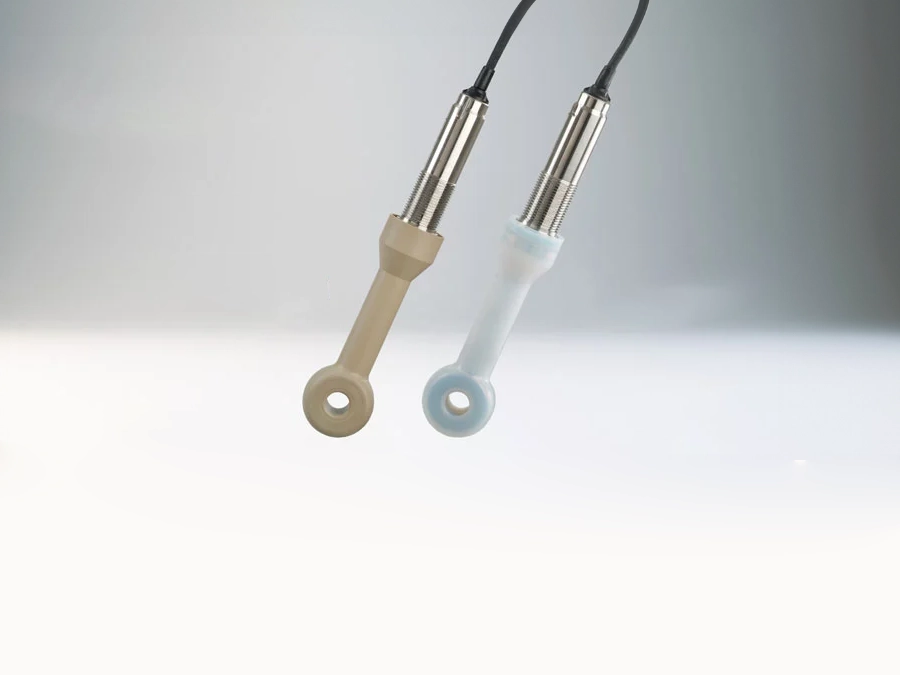
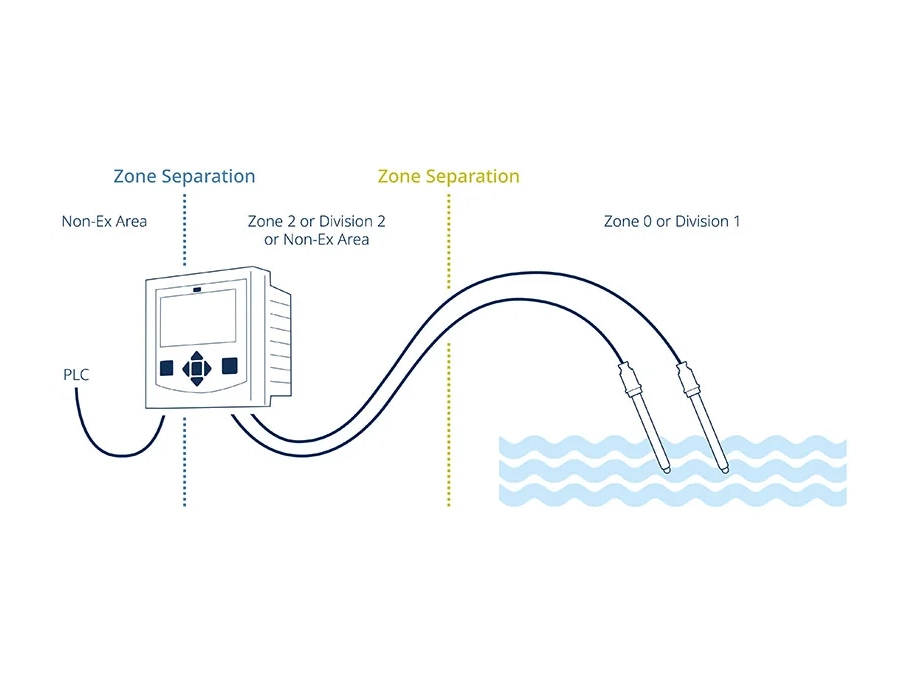
In these cases, digital Memosens sensors are the ideal solution. The contact-free plug-in connection of this sensor technology is completely resistant to wetness and contamination of all types. Thanks to the inductive transmission of energy and measured values, measured value distortion due to defective contacting is a thing of the past. Memosens sensors improve pH, ORP, oxygen, and conductivity measurements in utilities.
Return on Investment
- The contacting problems and measured value distortions typical of conventional analog sensors in moist or wet environments are eliminated with the perfect galvanic isolation of Memosens technology.
- The high reliability and accuracy of the measurements enable the careful metering of chemicals. With Memosens technology, users avoid economically inefficient overdosing, improve process quality, and extend the service life of plants in utilities.
- Precise conductivity measurements enable corrosion and leakage to be detected and eliminated early on, before expensive damage to plants and the environment occurs.
- The amount of time needed to replace sensors is dramatically reduced with Memosens. It is possible to pre-calibrate Memosens sensors in the laboratory, eliminating the need for time-intensive, unsafe, and expensive on-site calibration under difficult conditions.
H2 [Ind] <Keywords Industry> [Proc] [App] Application Description
[Ind] briefly: where can be used Knick products
[Proc]
[App] Detailed application description, why is measured, which customer problem is solved
H3 [App] Initial Situation
Was there a solution before, which was perhaps not good enough? Have requirements changed
H3 [App] Requirements of Application
What were the special or biggest requirements: Operating environment, legal requirements, medium, pressure, temperature, installation situation
H3 [App] Solution
Was a previous test necessary?
Associated Products
Associated Industries and Applications
Overview of specific applications and product solutions in different areas of power plants.